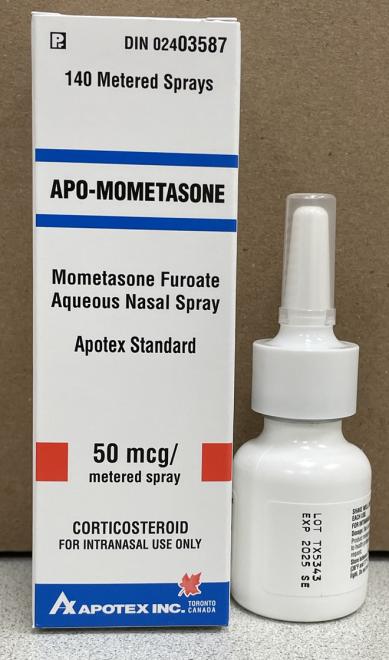
Medical Recall:
APO-Mometasone Nasal Spray
Have you been adversely affected by a product labelled for recall? Pushor Mitchell LLP’s Personal Injury team is here to support you. Click here to learn more.
Medical Recall News
Apotex Inc. is recalling two lots of APO-Mometasone nasal spray due to possible bacterial contamination with Burkholderia cepacia complex (Bcc).
Product: APO-Mometasone nasal spray, 50 mcg/metered spray
Issue: Contamination and risk of infection
What to do: Do not use the affected product. Seek medical attention if you or your child have used this product and are experiencing persistent or worsening symptoms, such as fevers, or facial pain or pressure.
If you or a loved one has experienced any of these symptoms following the use of APO-Mometasone nasal spray, do not return your medication to the pharmacy. Keep your supply in a non-refrigerated environment, and contact Bryan Fitzpatrick at Pushor Mitchell LLP for legal support.
Contact Bryan Fitzpatrick Now
Email Bryan at [email protected] or reach out via telephone at 250.869.1127.

Further information:
Apotex Inc. is recalling two lots of APO-Mometasone nasal spray due to possible bacterial contamination with Burkholderia cepacia complex (Bcc). Bcc is a group of bacteria that poses a low medical risk to most healthy people; however, children, those with chronic lung diseases, people who are pregnant, seniors and those with a weakened immune system may be at a higher risk of illness.
APO-Mometasone nasal spray is a prescription drug used to treat seasonal and year-round nasal allergy symptoms (such as itchy, stuffy or runny nose and sneezing) in children 3-11 years old. It is also used to treat sinusitis (sinus inflammation) in adults and children 12 years of age and older, and nasal polyps in adults.
The effects of Bcc vary widely, ranging from no symptoms at all to serious infections. In severe cases, Bcc can lead to bloodstream infections that may result in sepsis (a serious medical condition caused by an overwhelming immune response to an infection) and death. Bcc is often resistant to common antibiotics. People experiencing persistent or worsening symptoms, such as fevers, or facial pain or pressure, should seek medical attention.